UUID (Universally Unique IDentifier) 在 RFC4122 中定义,占用 16 字节空间,为方便阅读,通常将其表示为由-分隔的五组十六进制字符串。
-- PostgreSQL 13 增加了内置生成随机 UUID 的方法
postgres=# select gen_random_uuid();
gen_random_uuid
--------------------------------------
e6e12d78-8b1b-4c5c-90d2-e07dcbdbee73
(1 row)
RFC4122 定义了 5 个不同版本的 UUID,这些版本之间的区别在于生成 UUID 所需的输入和输出的位结构,当人们讨论 UUID 时,几乎总是指 UUIDv4:
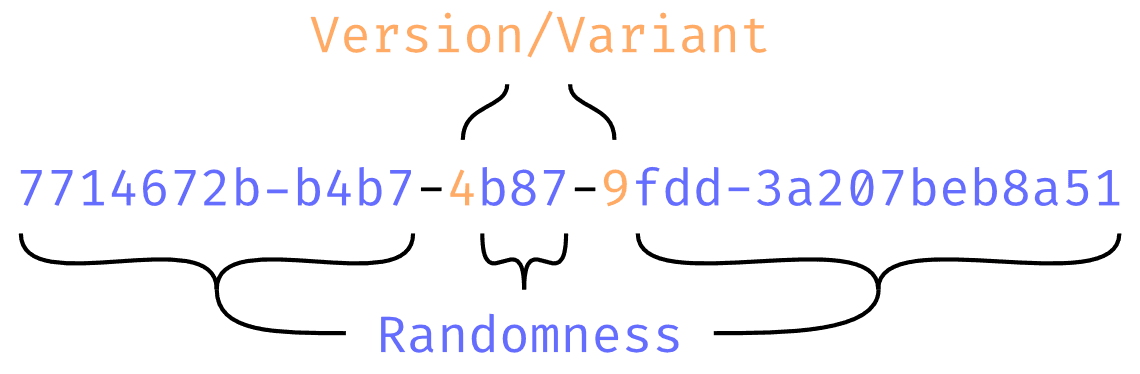
其结构中的第 7 个字节的高四位为版本号 0b0100, 第 9 个字节的高两位总是为 0b10,其余 122 位为随机值。因此无论用 SQL 还是命令行工具 uuidgen 生成的 UUID,其在上图中第一个橘色的位置始终为 4,第二个橘色的位置为 8, 9, a, b 中的一个。
contrib 下的 uuid-ossp extension 提供了生成五个版本 UUID 的函数。
UUIDv4 存在的问题
当用 UUIDv4 作为主键时,如果大量写入随机的 UUID 值,会导致 B-tree 更多的页面分裂,较低的 filling factor,大量的页面碎片(Fragmentation),占用更多的存储空间。当索引数据大于内存时,缓存命中率也会逐渐降低。由于写入分散,大量页面需要在 Checkpoint 之后写 FPI,进而导致 WAL 的写入放大,WAL 写入量的增加又会更频繁地触发 Checkpoint,又导致更多的 FPI 写入操作 🥺
UUIDv4 的随机性对于读操作同样有影响,由于数据失去了相关性,根据范围去查询 UUID 毫无意义。
对于 UUIDv4 存在的问题,Tomas Vondra 2018 年设计的 sequential-uuids 可以在不牺牲太多随机性的前提下以更顺序的模式生成 UUID,利用 sequence 或时间计算一个前缀来保证生成的 UUID 具有良好的局部性。Sequential UUID Generators 对 uuid-ossp 提供的 uuid_generate_v4 和该设计中的 uuid_time_nextval/uuid_sequence_nextval 进行了性能、WAL写入放大 及 缓存命中率的对比。
需要注意的是,sequential-uuids 生成的依然是 UUIDv4,并且需要用户决定传入的参数大小(block_size, block_count),使用起来并不是很方便。
UUIDv7
从 2022 年开始(最早的草案应该在 2020 年就提出了),IETF uuidrev 工作组对 UUID 的格式进行了更新,引入了 UUIDv6, UUIDv7 和 UUIDv8,截至目前,rfc4122bis 已经更新到了 version 14,可能很快会被接受为标准。
其中 UUIDv7 使用时间戳作为前缀,同时保留了 62 位的随机值:
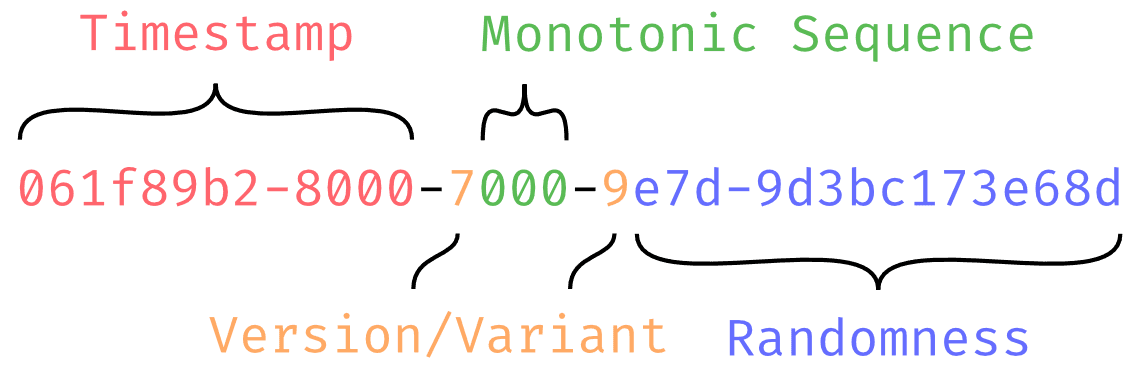
PG hackers 邮件列表已经有 patch 来支持生成 UUIDv7,极有可能在 PG17 中引入该特性(前提是 rfc4122bis 被接受为标准)。
将 patch 打到本地代码仓,连续生成几个 UUIDv7,可以看出生成的 uuid 具有良好的连续性:
postgres=# select gen_uuid_v7() from generate_series(1,5);
gen_uuid_v7
--------------------------------------
018c516f-e20a-737c-b338-864ebefc8c18
018c516f-e20a-737c-b4cf-64698e408f6f
018c516f-e20a-737c-b513-5e826a08d3db
018c516f-e20a-737c-b659-464de47f9bfe
018c516f-e20a-737c-b74f-323bbc64b029
(5 rows)
测试
我们参照 UNEXPECTED DOWNSIDES OF UUID KEYS IN POSTGRESQL 对 UUIDv4 和 UUIDv7 进行一个对比。
生成速度
postgres=# explain analyze select count(gen_random_uuid()) from generate_series(1, 1000000);
QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Aggregate (cost=15000.00..15000.01 rows=1 width=8) (actual time=10884.292..10884.293 rows=1 loops=1)
-> Function Scan on generate_series (cost=0.00..10000.00 rows=1000000 width=0) (actual time=90.128..255.612 rows=1000000 loops=1)
Planning Time: 0.853 ms
Execution Time: 10887.408 ms
(4 rows)
postgres=# explain analyze select count(gen_uuid_v7()) from generate_series(1, 1000000);
QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Aggregate (cost=15000.00..15000.01 rows=1 width=8) (actual time=10973.624..10973.625 rows=1 loops=1)
-> Function Scan on generate_series (cost=0.00..10000.00 rows=1000000 width=0) (actual time=90.129..266.464 rows=1000000 loops=1)
Planning Time: 0.029 ms
Execution Time: 10975.888 ms
(4 rows)
B-tree 索引写入性能及大小
postgres=# create table records (id int8 not null, uuid_v4 uuid not null, uuid_v7 uuid not null, filler text);
CREATE TABLE
postgres=# insert into records select id, gen_random_uuid(), gen_uuid_v7(), repeat(' ', 100) from generate_series(1, 1000000) id;
INSERT 0 1000000
Time: 23570.256 ms (00:23.570)
postgres=# create index on records (uuid_v4);
CREATE INDEX
Time: 736.436 ms
postgres=# create index on records (uuid_v7);
CREATE INDEX
Time: 583.667 ms
BRIN index
postgres=# drop index records_uuid_v4_idx ;
DROP INDEX
Time: 4.853 ms
postgres=# drop index records_uuid_v7_idx ;
DROP INDEX
postgres=# create index records_uuid_v4_brin_idx on records using BRIN (uuid_v4);
CREATE INDEX
Time: 105.737 ms
postgres=# create index records_uuid_v7_brin_idx on records using BRIN (uuid_v7);
CREATE INDEX
Time: 115.418 ms
postgres=# select id, uuid_v4, uuid_v7 from records limit 1;
id | uuid_v4 | uuid_v7
----+--------------------------------------+--------------------------------------
1 | 70548b99-f3c4-437d-89f9-7ac1c96b7975 | 018c517e-b568-77a6-89d4-ccfb0af12fd1
(1 row)
Time: 0.188 ms
postgres=# set enable_seqscan TO false;
SET
postgres=# SET max_parallel_workers_per_gather = 0;
SET
postgres=# explain analyze select * from records where uuid_v4 = '70548b99-f3c4-437d-89f9-7ac1c96b7975';
QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Bitmap Heap Scan on records (cost=17.34..33794.34 rows=1 width=141) (actual time=0.461..138.931 rows=1 loops=1)
Recheck Cond: (uuid_v4 = '70548b99-f3c4-437d-89f9-7ac1c96b7975'::uuid)
Rows Removed by Index Recheck: 999999
Heap Blocks: lossy=21277
-> Bitmap Index Scan on records_uuid_v4_brin_idx (cost=0.00..17.34 rows=1000000 width=0) (actual time=0.445..0.445 rows=212770 loops=1)
Index Cond: (uuid_v4 = '70548b99-f3c4-437d-89f9-7ac1c96b7975'::uuid)
Planning Time: 0.055 ms
Execution Time: 138.951 ms
(8 rows)
postgres=# explain analyze select * from records where uuid_v7 = '018c517e-b568-77a6-89d4-ccfb0af12fd1';
QUERY PLAN
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Bitmap Heap Scan on records (cost=12.03..13263.31 rows=1 width=141) (actual time=0.077..0.710 rows=1 loops=1)
Recheck Cond: (uuid_v7 = '018c517e-b568-77a6-89d4-ccfb0af12fd1'::uuid)
Rows Removed by Index Recheck: 6015
Heap Blocks: lossy=128
-> Bitmap Index Scan on records_uuid_v7_brin_idx (cost=0.00..12.03 rows=5988 width=0) (actual time=0.069..0.069 rows=1280 loops=1)
Index Cond: (uuid_v7 = '018c517e-b568-77a6-89d4-ccfb0af12fd1'::uuid)
Planning Time: 0.057 ms
Execution Time: 0.728 ms
(8 rows)
结论
- UUIDv7 在生成速度上稍逊于 UUIDv4,当然也可把 UUID 的生成交给客户端来完成
- UUIDv7 生成的 B-tree 占用空间小于 UUIDv4
- 由于 UUIDv7 的顺序性,BRIN 的过滤效果远远好于 UUIDv4
- bloom filter 可用于优化 UUIDv4 的 BRIN,但这不在本文讨论范围,请参考 Unconventional ways to index UUIDs in PostgreSQL