Patroni 是一个用 Python 实现,用来部署、管理和监控 PostgreSQL 高可用(HA)集群的开源工具。本文对 Patroni 代码的核心模块进行简要介绍。
术语澄清
自 Patroni 3.0 可以管理 Citus 之后,Patroni 涉及了更多的 Cluster 术语,我觉得有必要在这里澄清一下,以消除理解上的偏差。
- Database cluster: 由一个 PG 实例管理的多个 databases,也称作 PostgreSQL Instance 或 PostgreSQL 节点
- PostgreSQL cluster: 多个 PostgreSQL Instance 构成的一主多备的拓扑结构
- Citus cluster: 一个角色为 Coordinator 的 PostgreSQL cluster 和多个角色为 Worker 的 PostgreSQL cluster 构成的 MPP 架构
- Patroni cluster: 泛指 Patroni 管理的集群,PostgreSQL cluster 和 Citus cluster 都可叫作 Patroni cluster
从 Patroni 中 Cluster 类的定义也能看出 Patroni cluster 可以代表 PostgreSQL cluster 和 Citus cluster 两类集群,对于非 Citus 集群而言,下面结构的 workers 字段为 None。
class Cluster(NamedTuple('Cluster',
[('initialize', Optional[str]),
('config', Optional[ClusterConfig]),
('leader', Optional[Leader]),
('status', Status),
('members', List[Member]),
('failover', Optional[Failover]),
('sync', SyncState),
('history', Optional[TimelineHistory]),
('failsafe', Optional[Dict[str, str]]),
('workers', Dict[int, 'Cluster'])])):
另外,由于 Patroni 进程和其管理的 PostgreSQL Instance 是绑定在一起的,有时候会将二者统一称作 Patroni Instance。
部署形态
部署 Patroni 首先需要一个分布式配置管理服务(Distributed Configuration Service),能够提供以下能力:
- 实现共识算法,在任意时间点提供一致的、single source of truth 的数据存储
- 支持 Compare-and-Set 操作
- 提供 Sessions/Lease/TTL 等机制来失效键值
- 提供用于订阅并接收特定键更改的 Watch API
前两个能力是必需的,后两个如果没有 Patroni 也能工作。Patroni 支持的配置管理服务有:
- etcd
- Consul
- ZooKeeper
- Kubernetes API
有了 DCS 之后,只需写好配置文件,就可以启动 Patroni 进程(Patroni 进程所在的环境需要安装 PostgreSQL 必需的二进制),Patroni 负责 PostgreSQL 实例的全部生命周期。一个典型的 Patroni 集群架构图如下所示(配置文件见附录):
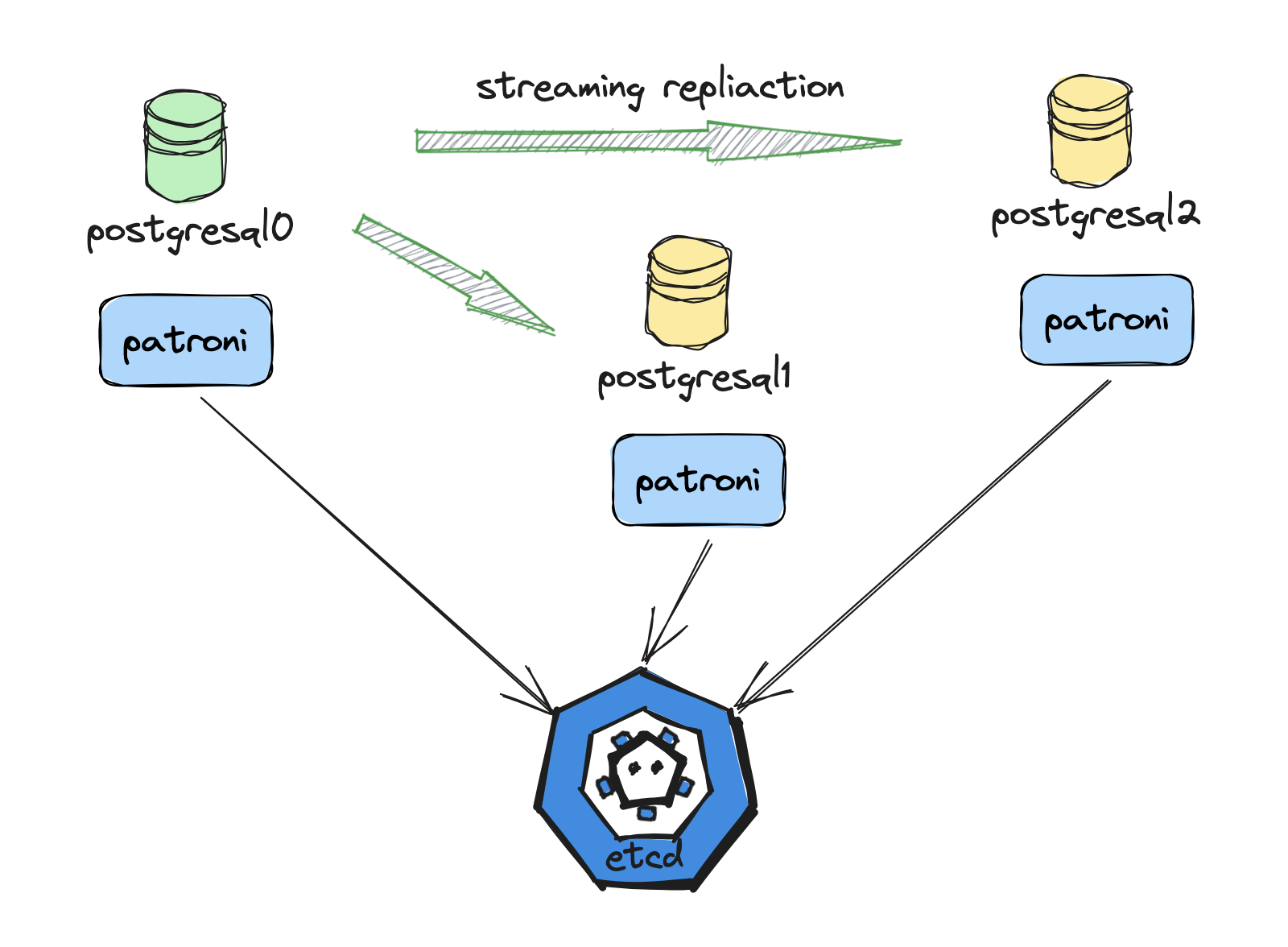
核心模块
Patroni 的核心代码包含两部分,一部分是常驻后台的 patroni 进程,另一部分是与 restapi 交互的命令行工具 patronictl。本文只介绍 patroni 相关的内容。
从 Patroni 的构造函数可以看出,它包含如下几个子模块,我们依次介绍。
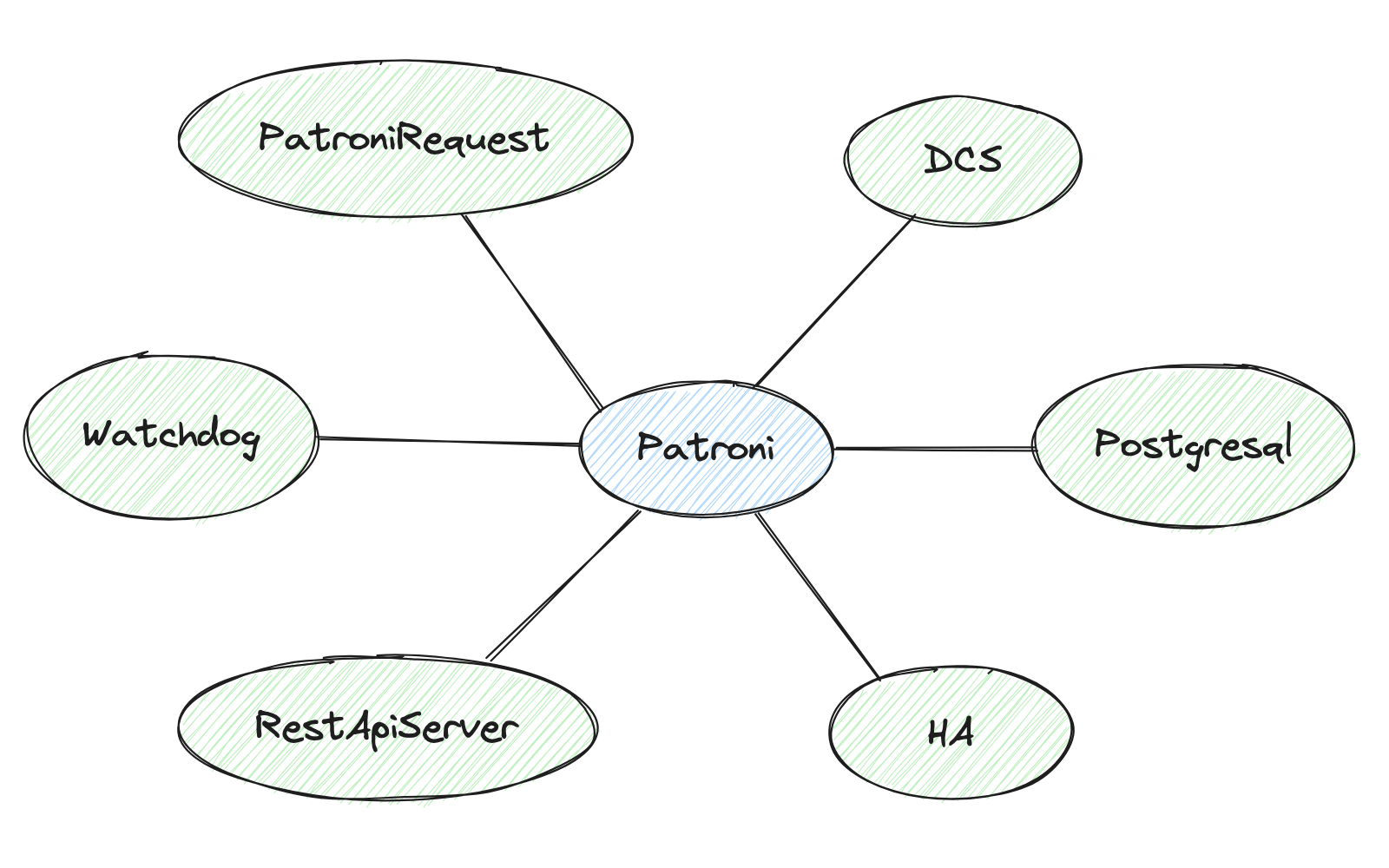
PatroniRequest
向 restapi 发送请求的辅助类,通常用于 patronictl 与 patroni restapi 之间的交互及获取其它节点的状态,Patroni 3.0 之后,还用于向 Citus Coordinator 发送节点变更信息,Coordinator 根据收到的消息修改 pg_dist_node 元信息。
Watchdog
为了解决脑裂问题(split-brain),Patroni 需要保证当 leader key 失效后对应的 PostgreSQL 实例不再接受任何事务请求,通常 Patroni 会发出停止 PG 的命令。但实际使用中可能会遇到一些问题导致实例停止失败,如:
- Patroni 由于自身 bug、OOM 或被系统管理员意外杀死等原因停止运行
- 停止 PostgreSQL 过程过于漫长
- 在负载高的 OS 上 Patroni 得不到调度
Watchdog 是解决这个问题的第二道防线。Patroni 在将 PostgreSQL Instance promote 为 primary 前激活 watchdog,并在之后处于 primary 的过程中持续发送心跳给 watchdog。当出现问题导致 watchdog 在一定时间段内收不到心跳后,watchdog 会重置整个系统以防止脑裂的出现。
RestApiServer
暴露一系列 rest 接口供 patronictl 和其它 Patroni Instance 访问。
DCS (Distributed Configuration Store)
Patroni 依赖 DCS 来发现 PostgreSQL Cluster 的其它节点以及配置流复制,DCS 存储的内容可以抽象为一个目录层级,如上述的集群存储在 DCS 的目录结构为:
service
|-- batman
|-- config
|-- status
|-- history
|-- initialize
|-- leader
+-- members
|-- postgresql0
|-- postgresql1
+-- postgresql2
在 Patroni Cluster 的生命过程当中,除上述文件外还可能会有 failover、sync 和 failsafe,它们会在 _load_cluster 请求中被加载到 Cluster 类,其中各个文件保存的内容也会解析到对应的类中。
为了支持多种配置服务,DCS 提供了一个抽象类 AbstractDCS,定义了六类接口供具体的 DCS 类来实现:
- 需要在 retry_timeout 时间内完成,以防止 DCS 被认为不可访问的函数,会返回构造复杂的数据对象
# 处理存储在 DCS 的数据并构造 Cluster 对象
AbstractDCS._cluster_loader
AbstractDCS._citus_cluster_loader
AbstractDCS._load_cluster
- 同样在请求时间上有严格要求,并且在实现时需要注意 ACID 事务特性的函数
# 创建和更新 leader
AbstractDCS.attempt_to_acquire_leader
AbstractDCS._update_leader
- 需要依赖 Compare-and-Set 来保证只有一个 member 创建 key 的函数
# 创建 initialze
AbstractDCS.initialize
- 一些需要实现的 getter 和 setter 函数
AbstractDCS.take_leader: method to create a new leader key in the DCS.
AbstractDCS.set_ttl: method for setting TTL value in DCS.
AbstractDCS.ttl: property which returns the current TTL.
AbstractDCS.set_retry_timeout: method for setting ``retry_timeout`` in DCS backend.
AbstractDCS._write_leader_optime: compatibility method to write WAL LSN to DCS.
AbstractDCS._write_status: method to write WAL LSN for slots to the DCS.
AbstractDCS._write_failsafe: method to write cluster topology to the DCS, used by failsafe mechanism.
AbstractDCS.touch_member: method to update individual member key in the DCS.
AbstractDCS.set_history_value: method to set the ``history`` key in the DCS.
- 需要使用 Compare-and-Set 来实现的一些 setter
AbstractDCS.set_failover_value: method to create and/or update the ``failover`` key in the DCS.
AbstractDCS.set_config_value: method to create and/or update the ``failover`` key in the DCS.
AbstractDCS.set_sync_state_value: method to set the synchronous state ``sync`` key in the DCS.
- 删除 DCS 中数据的方法
AbstractDCS.delete_sync_state
AbstractDCS.delete_cluster
AbstractDCS._delete_leader
AbstractDCS.cancel_initialization
我们看一个具体实现 Etcd 用到 Compare-and-Set 的方法:
@catch_etcd_errors
def initialize(self, create_new: bool = True, sysid: str = "") -> bool:
return bool(self.retry(self._client.write, self.initialize_path, sysid, prevExist=(not create_new)))
如果 create_new 为 True,则需要之前不存在(preExist = False)才能创建成功。
Postgresql
Postgresql 封装了与 PostgreSQL 相关的所有操作,包括初始化实例、basebackup、创建 replication slot、设置 synchronous_standby_names 等操作,HA 会根据集群状态调用该模块提供的各种方法。
Postgresql 类在一些方法中安插了一些钩子函数,当配置了对应的 callback 后,能在合适的时机执行 callback 来完成一些用户执行的操作。支持的 callback 类型有:
- ON_START: 在 Postgresql.start 函数中调用
- ON_STOP: 在 Postgresql.stop 函数中调用
- ON_RESTART: 在 Postgresql.restart 函数中调用
- ON_ROLE_CHANGE: 在 Postgresql.follow 和 Postgresql.promote 函数中调用
另外还可以指定 pre_promote、before_stop 用户想要执行的操作。这些能力使得 Patroni 使用起来非常灵活,用户可以根据自己的需求定制自己想要的功能。
Ha
Ha 是将其它模块串起来并完成 Patroni 逻辑的模块,事实上,Patroni 是通过周期性地(loop_wait 超时时间到 或 DCS watch 的 key 发生变化)调用 Ha 的 _run_cycle 函数来完成集群管理的。_run_cycle 的逻辑如下图所示:
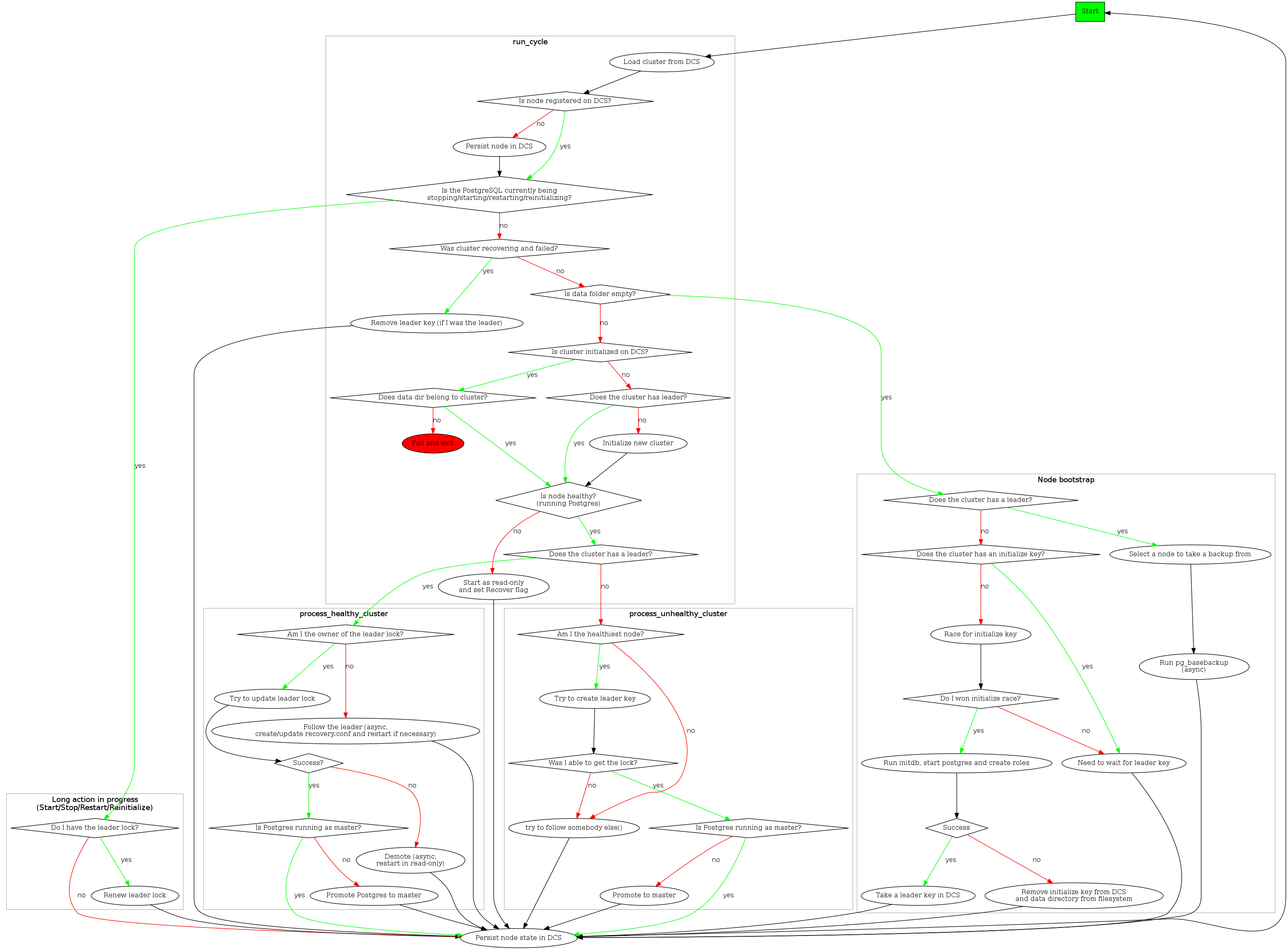
集群创建流程:
- 当集群创建的时候,每个 Patroni 进程将自己的 name 调用 touch_member 写入 DCS 的 /members 中,然后去创建 /initialize
- 只有一个 Patroni 创建 /initialize 会返回成功(CAS 保证),该实例调用 initdb 初始化实例,实例启动成功后去获取 leader key,并将 system identifier 写入到 DCS 的 /initialize 中
- 其它 Patroni 则等待这个实例创建成功后 follow 这个 leader
选新主:
如果集群不存在 /leader 锁时,每个 Patroni 实例通过对比自身 wal_position 和其它 member 的 wal_position 来确定自己是不是最健康的候选者(Ha.is_healthiest_node),如果自己是最佳选项,则尝试去获取 /leader 锁(可能有多个 member 同时认为自己是最佳选项,因此该操作需要 CAS 来保证只有一个实例获取锁),并把自己的 PG 实例 promote 成主。
其它 Patroni 实例则调用 follow 将自己的变为 Standby。
健康集群:
集群在健康时,Primary 会更新 /leader 锁的有效期,每个节点在处理的最后都会调用 touch_member 更新 PG 实例的信息,适用 etcdctl 可以查看对应节点的信息:
etcdctl get /service/batman/members/postgresql1
{"conn_url":"postgres://127.0.0.1:5433/postgres","api_url":"http://127.0.0.1:8009/patroni","state":"running","role":"replica","version":"3.1.2","xlog_location":117441640,"replication_state":"streaming","timeline":7}
Patroni 还有 failover/switchover、demote、recover 等操作,感兴趣的读者可以自行翻阅代码。
Citus
Citus 用一个名为 pg_dist_node 的 system catalog 来记录集群的节点信息,当 HA 检测自身节点角色变化时(promote 为主或 demote 为从),会调用 notify_citus_coordinator 将变更数据发送给 coordinator:
def notify_citus_coordinator(self, event: str) -> None:
if self.state_handler.citus_handler.is_worker():
coordinator = self.dcs.get_citus_coordinator()
if coordinator and coordinator.leader and coordinator.leader.conn_url:
try:
data = {'type': event,
'group': self.state_handler.citus_handler.group(),
'leader': self.state_handler.name,
'timeout': self.dcs.ttl,
'cooldown': self.patroni.config['retry_timeout']}
timeout = self.dcs.ttl if event == 'before_demote' else 2
self.patroni.request(coordinator.leader.member, 'post', 'citus', data, timeout=timeout, retries=0)
except Exception as e:
logger.warning('Request to Citus coordinator leader %s %s failed: %r',
coordinator.leader.name, coordinator.leader.member.api_url, e)
Coordinator 对应的 Patroni 在接收到请求后创建一个任务放到 CitusHandler 的任务链表中,CitusHandler 维护一个线程循环处理这些任务。
Patroni 还负责实例启动后创建 Citus 运行的 database 和 citus extension。
小结
Patroni 是一个颇受欢迎的 PostgreSQL HA 解决方案,Microsoft 甚至将 Citus 的集群管理放到了 Patroni 中。Patroni 的代码有些地方耦合度较高,比如 DCS 模块里充斥着很多 Citus 相关的代码,我认为如果这个改进一下,Patroni 应该可以接管更多 MPP 架构的 PG 系数据库。
附录
postgresql0
scope: batman
name: postgresql0
restapi:
listen: 127.0.0.1:8008
connect_address: 127.0.0.1:8008
etcd:
host: 127.0.0.1:2379
bootstrap:
# This section will be written into Etcd:/<namespace>/<scope>/config after initializing new cluster
# and all other cluster members will use it as a `global configuration`.
# WARNING! If you want to change any of the parameters that were set up
# via `bootstrap.dcs` section, please use `patronictl edit-config`!
dcs:
ttl: 30
loop_wait: 10
retry_timeout: 10
maximum_lag_on_failover: 1048576
postgresql:
use_pg_rewind: true
pg_hba:
- host replication replicator 127.0.0.1/32 md5
- host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
initdb: # Note: It needs to be a list (some options need values, others are switches)
- encoding: UTF8
- data-checksums
users:
admin:
password: admin%
options:
- createrole
- createdb
postgresql:
listen: 127.0.0.1:5432
connect_address: 127.0.0.1:5432
data_dir: data/postgresql0
pgpass: /tmp/pgpass0
authentication:
replication:
username: replicator
password: rep-pass
superuser:
username: postgres
password: zalando
rewind: # Has no effect on postgres 10 and lower
username: rewind_user
password: rewind_password
parameters:
unix_socket_directories: '..' # parent directory of data_dir
tags:
nofailover: false
noloadbalance: false
clonefrom: false
nosync: false
postgresql1
scope: batman
name: postgresql1
restapi:
listen: 127.0.0.1:8009
connect_address: 127.0.0.1:8009
etcd:
host: 127.0.0.1:2379
bootstrap:
# This section will be written into Etcd:/<namespace>/<scope>/config after initializing new cluster
# and all other cluster members will use it as a `global configuration`.
# WARNING! If you want to change any of the parameters that were set up
# via `bootstrap.dcs` section, please use `patronictl edit-config`!
dcs:
ttl: 30
loop_wait: 10
retry_timeout: 10
maximum_lag_on_failover: 1048576
postgresql:
use_pg_rewind: true
pg_hba:
- host replication replicator 127.0.0.1/32 md5
- host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
initdb: # Note: It needs to be a list (some options need values, others are switches)
- encoding: UTF8
- data-checksums
postgresql:
listen: 127.0.0.1:5433
connect_address: 127.0.0.1:5433
data_dir: data/postgresql1
pgpass: /tmp/pgpass1
authentication:
replication:
username: replicator
password: rep-pass
superuser:
username: postgres
password: zalando
rewind: # Has no effect on postgres 10 and lower
username: rewind_user
password: rewind_password
parameters:
unix_socket_directories: '..' # parent directory of data_dir
basebackup:
- verbose
- max-rate: 100M
tags:
nofailover: false
noloadbalance: false
clonefrom: false
postgresql2
scope: batman
name: postgresql2
restapi:
listen: 127.0.0.1:8010
connect_address: 127.0.0.1:8010
etcd:
host: 127.0.0.1:2379
bootstrap:
# This section will be written into Etcd:/<namespace>/<scope>/config after initializing new cluster
# and all other cluster members will use it as a `global configuration`.
# WARNING! If you want to change any of the parameters that were set up
# via `bootstrap.dcs` section, please use `patronictl edit-config`!
dcs:
ttl: 30
loop_wait: 10
retry_timeout: 10
maximum_lag_on_failover: 1048576
postgresql:
use_pg_rewind: true
pg_hba:
- host replication replicator 127.0.0.1/32 md5
- host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
initdb: # Note: It needs to be a list (some options need values, others are switches)
- encoding: UTF8
- data-checksums
postgresql:
listen: 127.0.0.1:5434
connect_address: 127.0.0.1:5434
data_dir: data/postgresql2
pgpass: /tmp/pgpass2
authentication:
replication:
username: replicator
password: rep-pass
superuser:
username: postgres
password: zalando
rewind: # Has no effect on postgres 10 and lower
username: rewind_user
password: rewind_password
parameters:
unix_socket_directories: '..' # parent directory of data_dir
tags:
nofailover: false
noloadbalance: false
clonefrom: false